A healthy and balanced diet is the cornerstone of good health. It provides the nutrients your body needs to function optimally, boosts your immune system, and supports overall well-being. However, with so much conflicting information out there, it can be challenging to know what constitutes a truly healthy diet. In this post, we’ll break down how to create a balanced diet that supports long-term health, improves energy levels, and helps you feel your best.
What Does a Balanced Diet Mean?
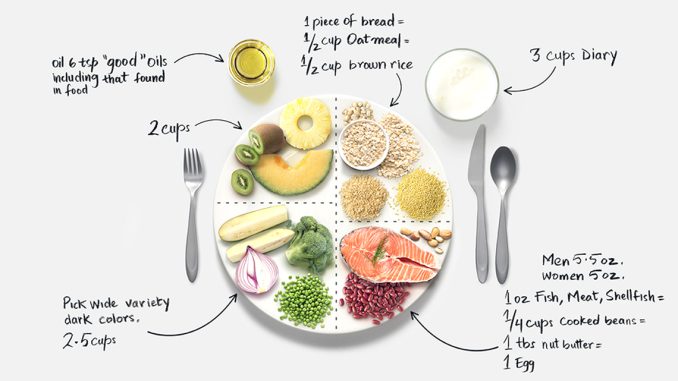
A balanced diet is one that provides the body with all the essential nutrients in the right proportions to maintain health and well-being. It’s not about restrictive eating or following trendy diets, but rather about consuming a variety of foods that supply the necessary macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals).
A healthy diet helps regulate body weight, supports proper digestion, improves brain function, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
The Key Components of a Balanced Diet
To create a balanced diet, it’s important to understand the role of different food groups and how they contribute to your health. The main components of a balanced diet include:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They provide fuel for the brain, muscles, and organs. The key is to focus on healthy carbs, which are found in foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-wheat bread are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates, which are digested more slowly, providing sustained energy.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These provide not only carbohydrates but also essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Aim for a colorful variety to ensure you’re getting a broad range of nutrients.
Tip: Try to replace refined grains (like white bread and pasta) with whole grains, as they have a lower glycemic index and provide more fiber.
2. Proteins
Protein is vital for tissue repair, muscle building, immune function, and hormone production. Including a variety of protein sources in your diet ensures that you’re getting all the essential amino acids your body needs.
- Animal Sources: Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy are all great sources of complete proteins.
- Plant-Based Sources: Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and quinoa are excellent sources of plant-based proteins. Combining different plant proteins can provide all the essential amino acids.
Tip: Aim to include both animal and plant-based proteins in your meals for a well-rounded nutrient profile.
3. Healthy Fats
Fat is essential for brain function, energy storage, and the absorption of certain vitamins (like A, D, E, and K). However, not all fats are created equal.
- Unsaturated Fats: These fats are found in foods like avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel). Unsaturated fats help lower bad cholesterol levels and support heart health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting brain health.
Tip: Limit saturated fats found in red meat and processed foods, as they can contribute to heart disease and high cholesterol.
4. Fiber
Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, as it helps with digestion, keeps you feeling full, and supports heart health. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble.
- Soluble Fiber: Found in oats, beans, apples, and carrots, soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar and lower cholesterol levels.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in whole grains, vegetables, and seeds, insoluble fiber helps prevent constipation and supports digestive health.
Tip: Aim for at least 25–30 grams of fiber per day, primarily from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
5. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential for a wide range of bodily functions, from immune health to bone strength and energy production. A healthy diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables will help ensure you’re getting a variety of micronutrients.
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens, vitamin C supports immune function and skin health.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is important for bone health and can be found in fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and exposure to sunlight.
- Calcium: Important for strong bones and teeth, calcium can be found in dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant milks.
Tip: Include a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole foods in your diet to cover all of your vitamin and mineral needs.
6. Water
Water is often overlooked, but it is essential for virtually every process in the body. It aids digestion, supports nutrient absorption, helps regulate body temperature, and flushes toxins from the system.
Tip: Aim for at least 8 glasses (2 liters) of water per day, and increase your intake if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
Tips for Creating a Healthy and Balanced Diet
Now that you know the key components of a balanced diet, here are some practical tips to help you put it all together:
1. Plan Your Meals
Meal planning is one of the best ways to ensure you’re eating a balanced diet. By planning ahead, you can ensure that each meal includes a variety of food groups and nutrients.
- Prep Your Meals: Preparing meals in advance can help you avoid unhealthy takeout options and ensure you’re eating nutritious foods throughout the week.
- Mix It Up: Include a variety of foods in your diet to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients. Rotate your fruits, vegetables, and protein sources to keep things interesting.
2. Focus on Whole Foods
The closer your food is to its natural state, the better it is for your health. Whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean meats, legumes, and whole grains are nutrient-dense and free from added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Limit your intake of processed snacks, sugary drinks, and packaged foods, as these often contain empty calories and unhealthy additives.
3. Practice Portion Control
Even healthy foods can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. Portion control is key to maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding overeating.
- Use Smaller Plates: This simple trick can help you reduce portion sizes and prevent overeating.
- Listen to Your Body: Eat when you’re hungry and stop when you’re full. Being mindful of your hunger cues can help you avoid overeating.
4. Include Healthy Snacks
Healthy snacks can help curb your hunger between meals and provide an energy boost. Opt for nutrient-dense snacks like:
- Fresh fruit
- Nuts and seeds
- Greek yogurt
- Veggie sticks with hummus
5. Balance Your Macronutrients
Try to balance your meals by including a combination of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates. A well-rounded meal keeps you feeling full longer and provides sustained energy throughout the day.